RADx–UP: An NIH COVID-19 Response Initiative
The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated existing health disparities among populations experiencing long-standing health inequities, including people from racial and ethnic minority groups and people living in underserved rural areas.
As part of its efforts to accelerate response to the excess morbidity and mortality impacting population groups disproportionately affected by COVID-19, National Institutes of Health (NIH) established collaborative initiatives across the agency to provide rapid response. The Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics–Underserved Populations (RADx–UP) program is part of NIH’s multifaceted response to the COVID-19 pandemic, and it is one of four components of the NIH RADx initiative to support innovative technologies to make millions of more rapid COVID-19 tests available, accessible, and easier to use for all Americans.
What is RADx–UP?
RADx–UP is a consortium of community-engaged research projects designed to assess and expand COVID-19 testing for populations disproportionately affected by, have the highest infection rates of, or are at increased risk for complications or poor health outcomes from COVID-19. These populations include (but are not limited to):
- People from racial and ethnic minority groups.
- People residing in nursing homes, jails, or underserved rural and urban areas.
- Pregnant people.
- People experiencing homelessness.
RADx–UP’s overarching goal is to understand the factors associated with disparities in COVID-19 morbidity and mortality and to reduce these disparities for disproportionately affected populations through improved access to and acceptance of testing. This goal aligns with NIMHD’s mission to improve minority health and reduce health disparities, which it does by leading and supporting related scientific research and programs. NIMHD co-leads the NIH-wide development and implementation of RADx–UP with the National Institute on Aging.
RADx–UP Implementation
RADx–UP has been implemented in three phases across communities in the United States and its territories as well as Tribal Nations—with 137 research projects and 1 coordination and data collection center (CDCC). NIMHD manages 44 of these research projects.
Phase I projects focus on community-engaged research to understand
COVID-19 testing patterns and to implement interventions to rapidly increase reach, access, acceptance, and uptake of FDA-approved COVID-19 diagnostics among populations disproportionately affected by COVID-19.
Phase II projects advance the scientific mission of the program and address new developments in the landscape of COVID-19 testing and diagnostic approaches, including:
- Addressing vaccine hesitancy and collaboration with NIH-funded Community Engagement Alliance against COVID-19 Disparities (CEAL) projects.
- Collaboration with those proposing innovative interventions to understand barriers and facilitators of testing.
- Implementation of evidence-based interventions to increase testing uptake.
Phase III projects further support evaluation of rapid testing interventions to prevent and control COVID-19 transmission and advance partnership-driven research in this area.
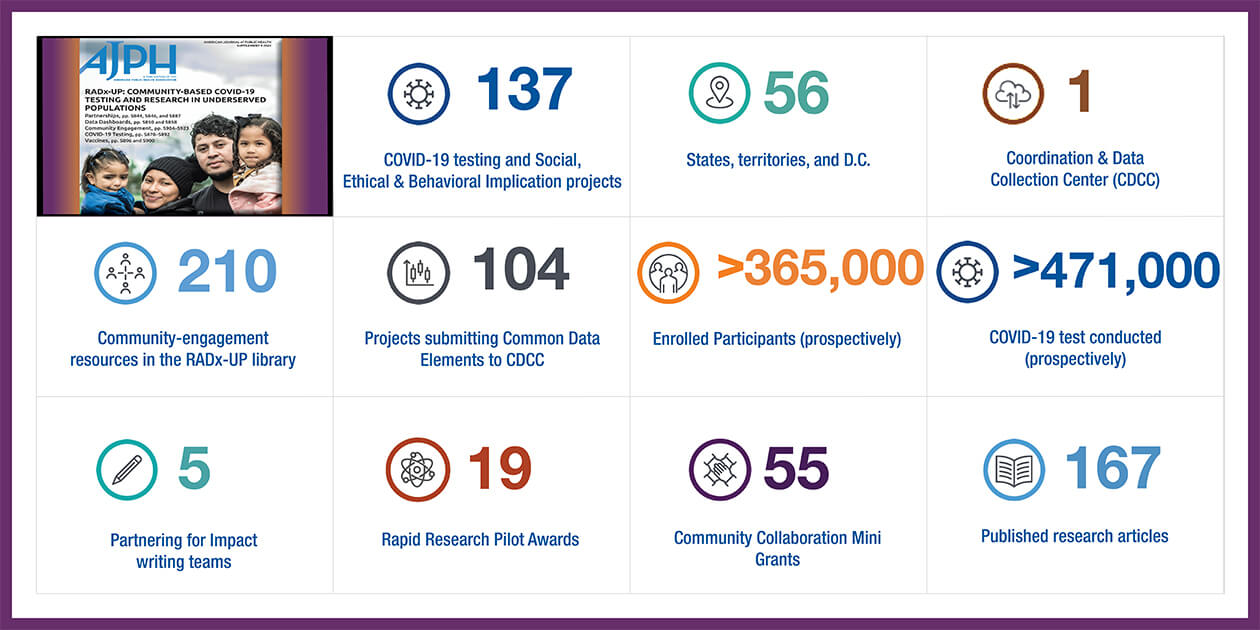
RADx–UP Overview
RADx–UP milestones as of January 2023:
- AJPH Supplement: RADx-UP: Community-Based COVID-19 Testing and Research in Underserved Population
- 137 COVID-19 testing and Social, Ethical and Behavioral Implication projects
- 56 States, territories, and D.C.
- Coordination and Data Collection Center (CDCC)
- 210 Community-engagement resources in the RADx-UP library
- 104 projects submitting Common Data Elements to the CDCC
- >365,000 enrolled participants (prospectively)
- >471,000 COVID-19 tests conducted (prospectively)
- 5 Partnering for Impact writing teams
- 19 Rapid Research Pilot awards
- 55 Community Collaboration mini grants
- 167 published research articles
Page updated Aug. 1, 2024 | published April 21, 2023